Topic 2 AP Exam Practice
Multiple-Choice Questions
Questions 1 to 3 refer to the map below.
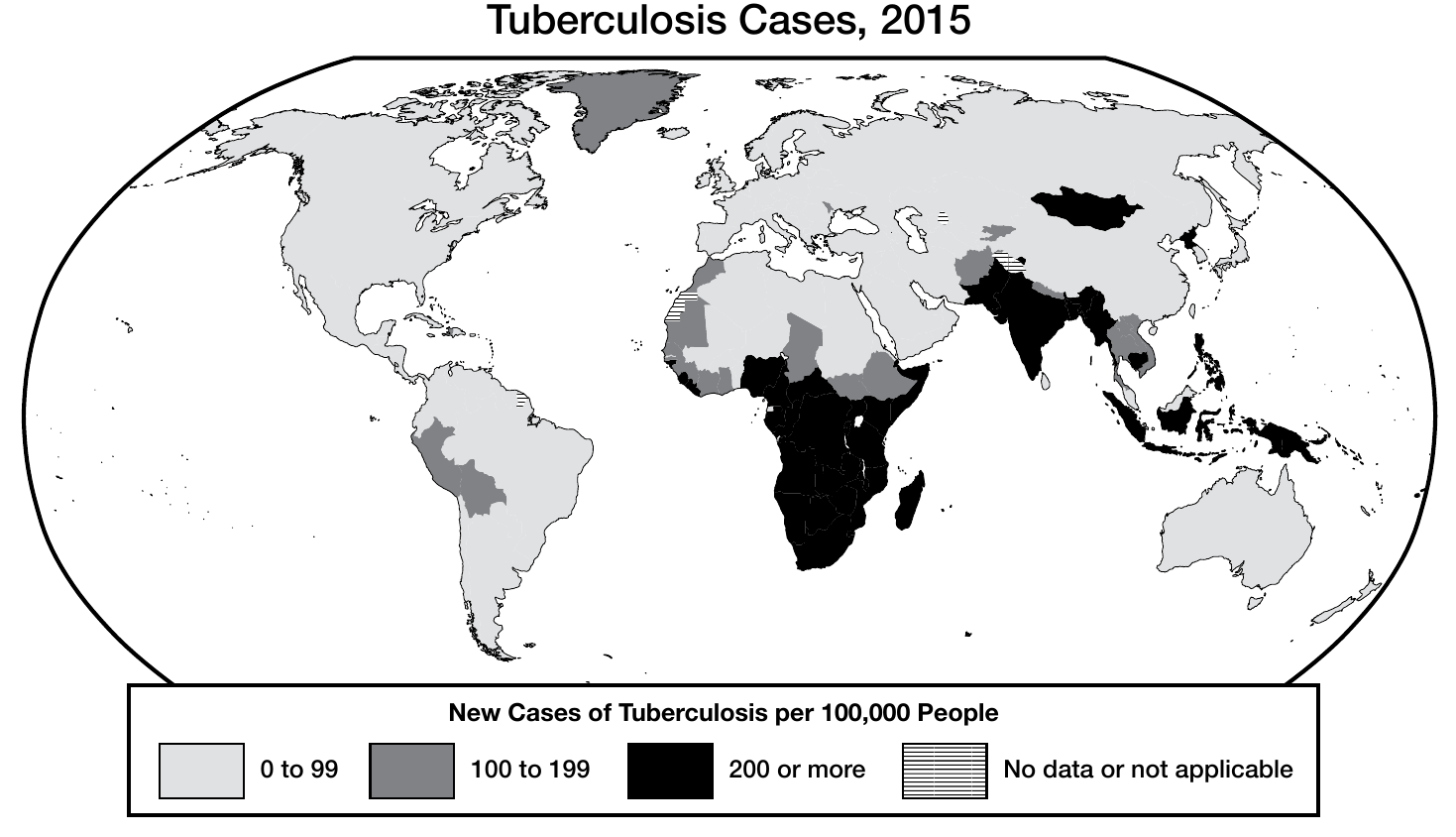
Tuberculosis is an infectious bacterial disease that spreads through the air.
1. Which of the following best explains the overall trend of tuberculosis cases shown on the map?
- (A) The role of trade routes in spreading disease
- (B) The lack of a global agency to coordinate public health campaigns
- (C) The spread of diseases in countries with rising birth rates
- (D) The persistence of diseases associated with poverty
2. Which of the following can be best be inferred about countries with the lowest rates of tuberculosis infection?
- (A) Climate conditions kill off the tuberculosis bacteria.
- (B) Medical workers control the spread of tuberculosis with antibiotics.
- (C) Scientific advances have ended the threat of new epidemic diseases.
- (D) These countries receive the lowest numbers of immigrants.
3. Which differences shown on the map most directly reflected which more general development in the late 20th century?
- (A) Longer life expectancy
- (B) Deforestation and desertification
- (C) Neocolonialism
- (D) The uneven expansion of Internet access
Short-Answer Questions
1. Use the passage below to answer all parts of the question that follows.
“The health problems faced by the world’s poorest populations are not caused by a lack of drugs specifically related to their problems and diseases. The real problem is ensuring that these populations can actually access vital medicines. Many governments fail their populations in this respect by imposing punitive tariffs and taxes on medicines, and by skewing their spending priorities in favour of defense over health. The governments of poor countries hinder the creation of wealth, imposing obstacles in the way of owning and transferring property, imposing unnecessary regulatory barriers on entrepreneurs and businesses, and restricting trade through extortionate tariffs . . . [leaving] poor populations without the necessary resources to access the medicines that could so easily transform their quality of life.
Emerging health threats, ranging from drug-resistant strains of AIDS and tuberculosis to avian flu, remind us of the importance of ensuring that the pharmaceutical industry continues to discover and develop new drugs. Innovation is a fragile process, and it can be weakened or thwarted by poor public policies.”
Phillip Stevens, Director of Health Projects, Diseases of Poverty and the 10/90 Gap, 2004
2. Answer all parts of the question that follows.